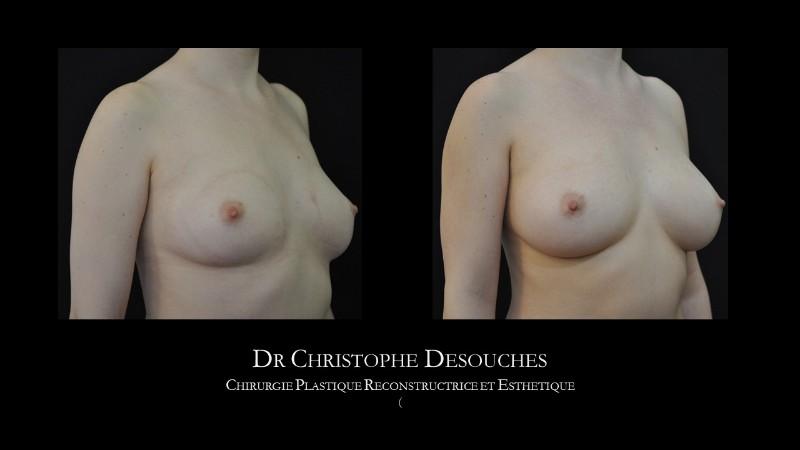
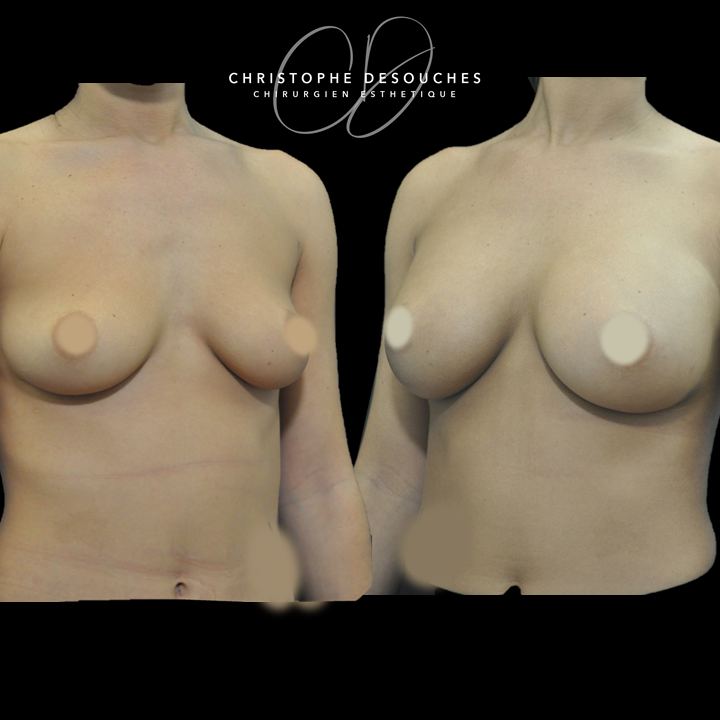
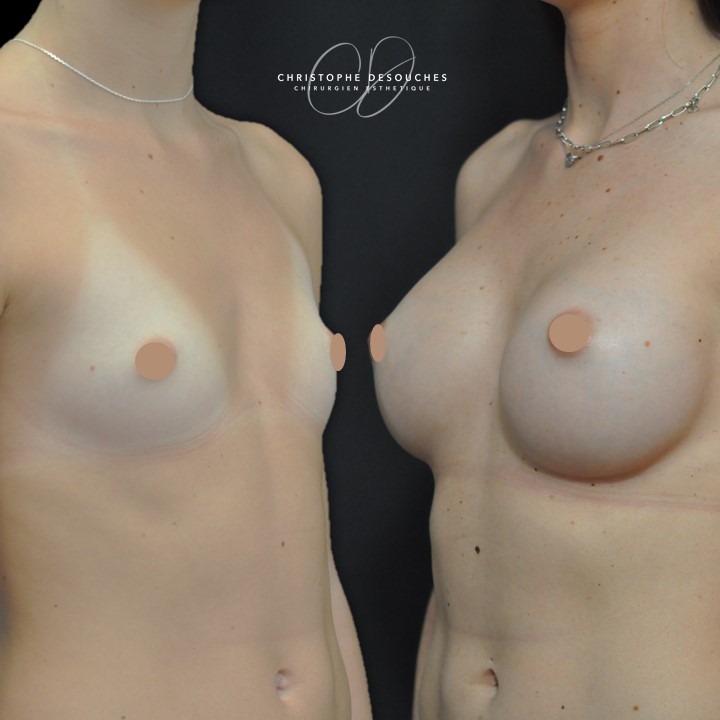
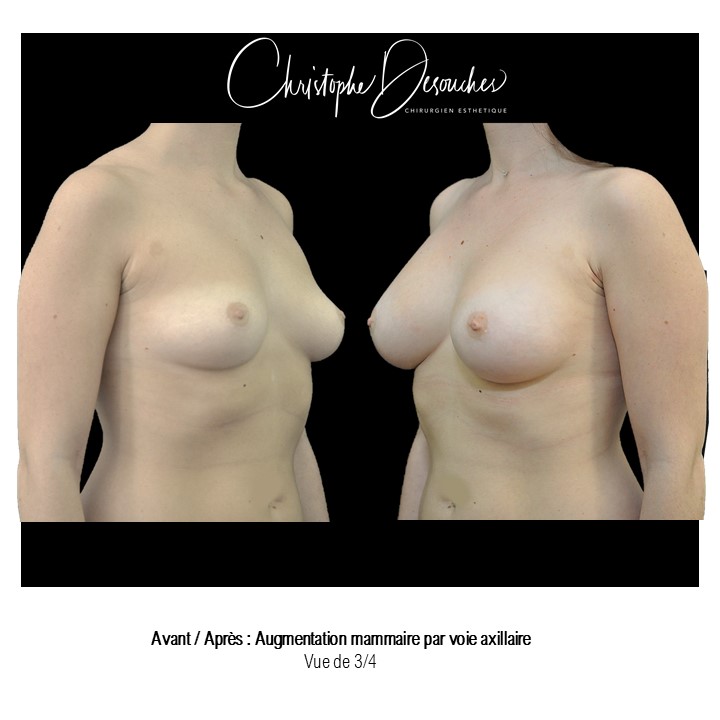
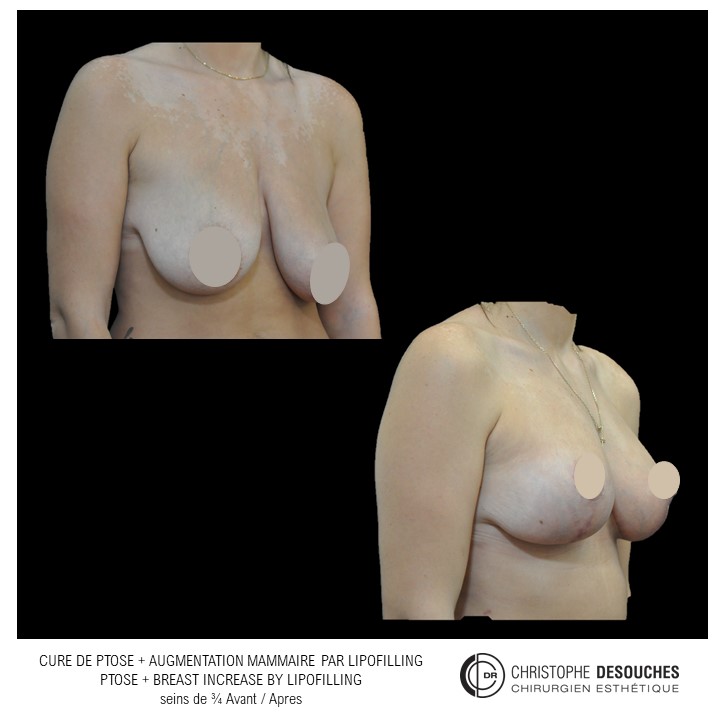
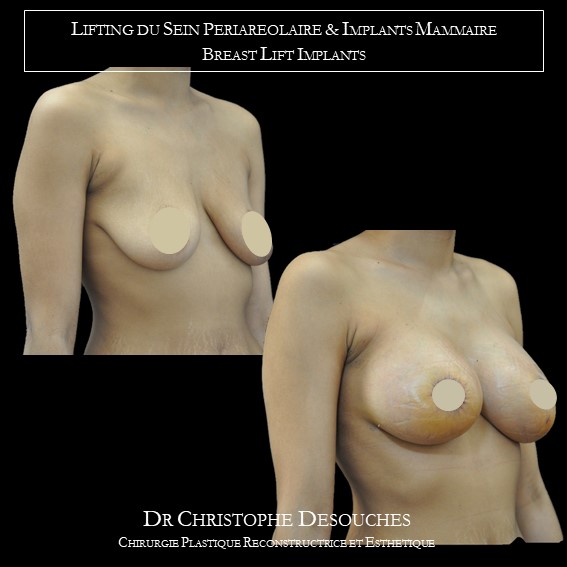
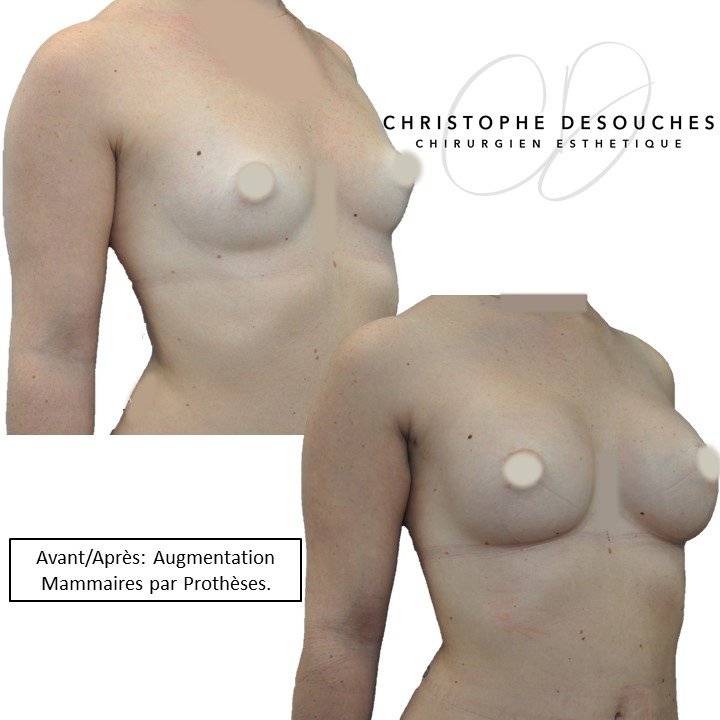
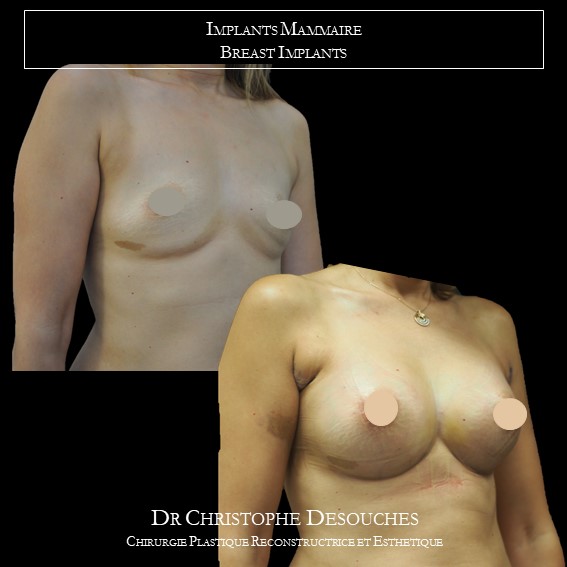
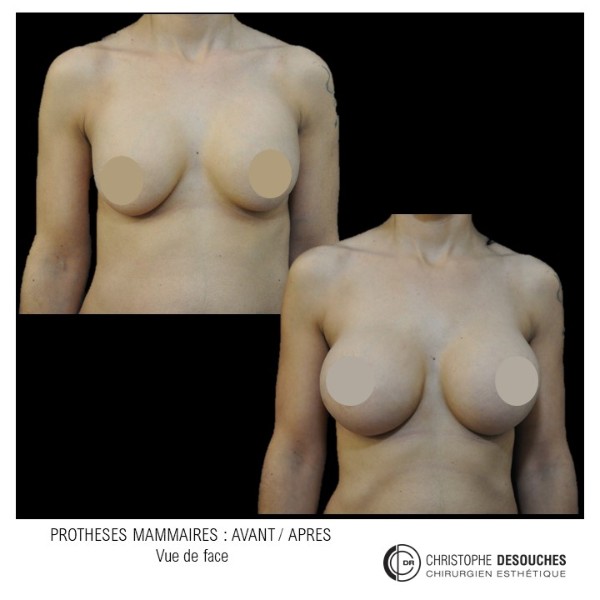
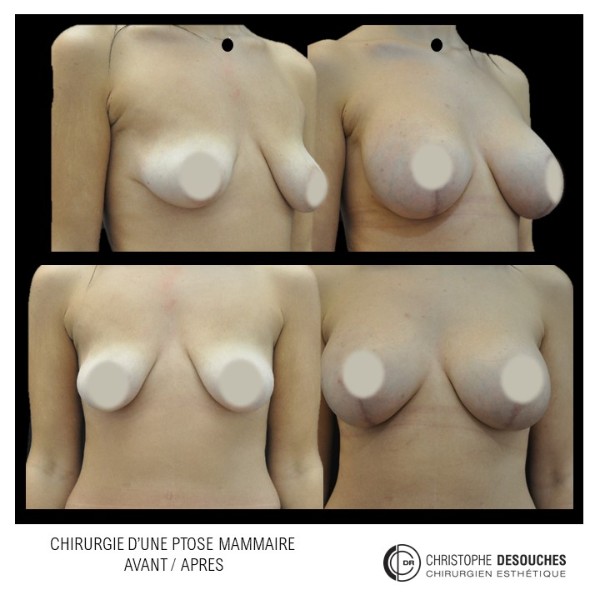
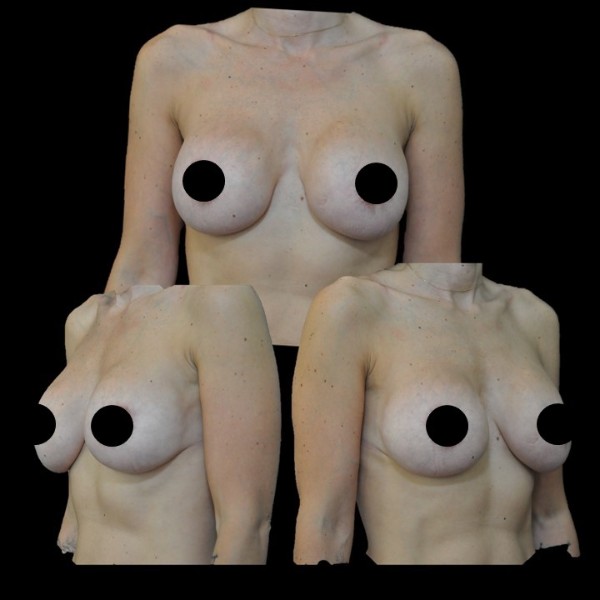
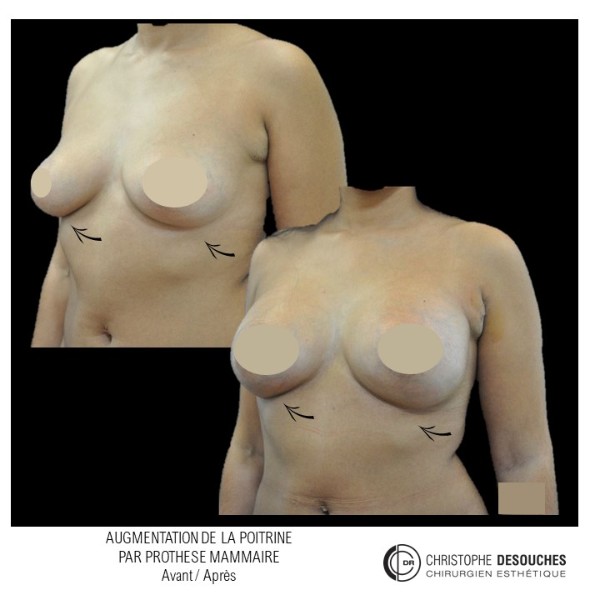
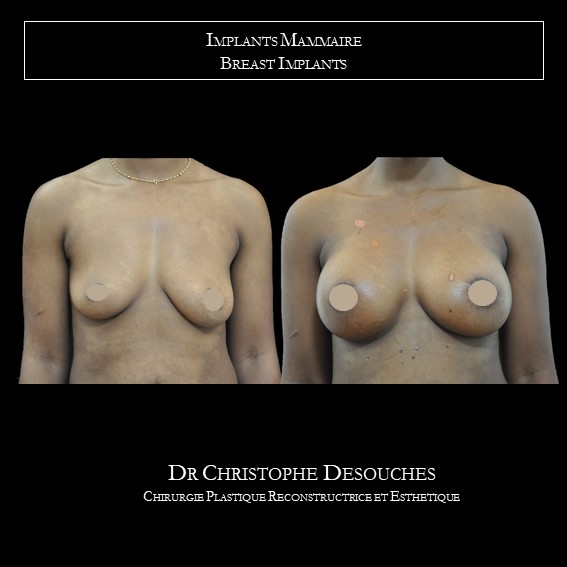
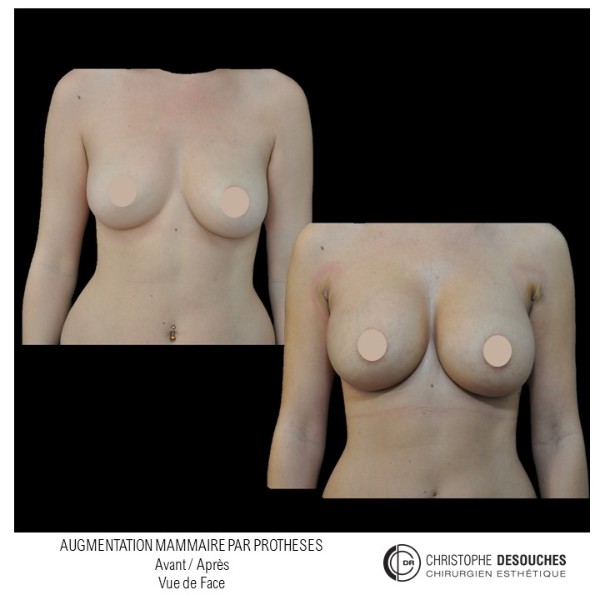
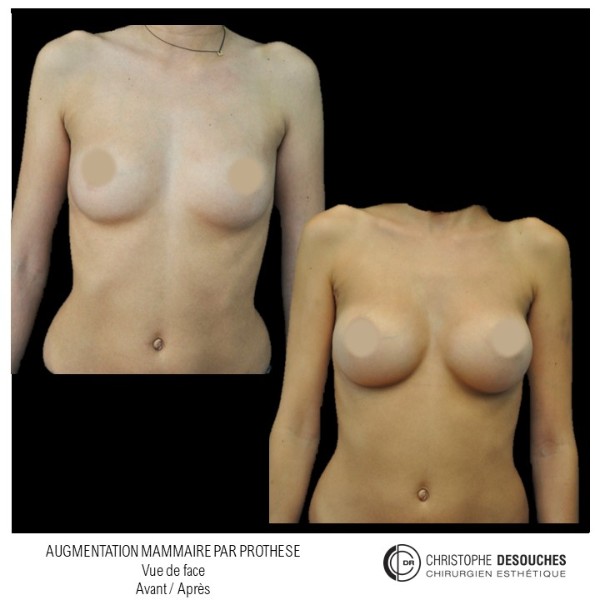
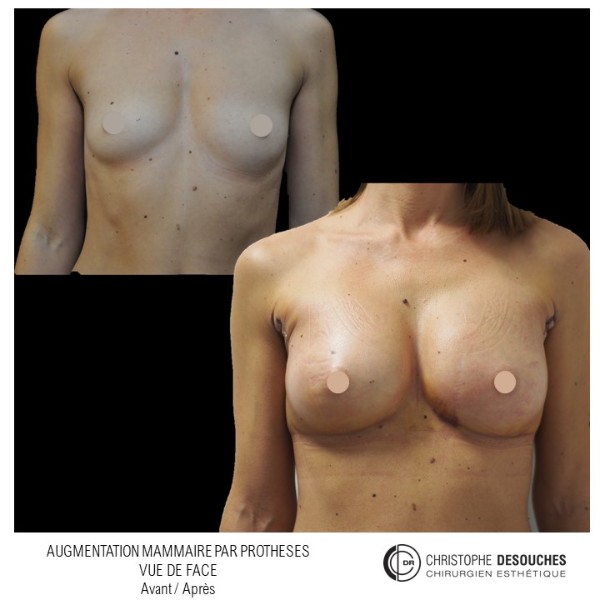
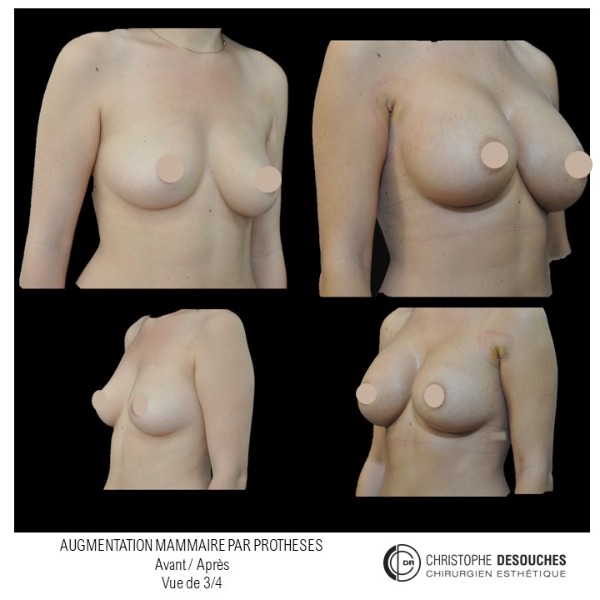
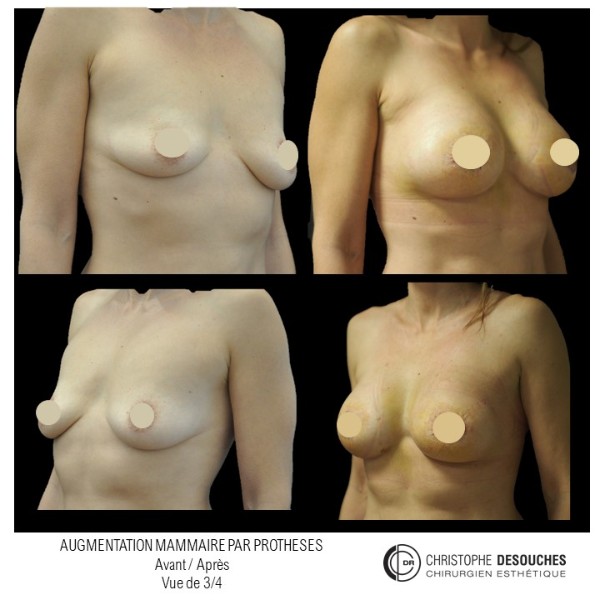
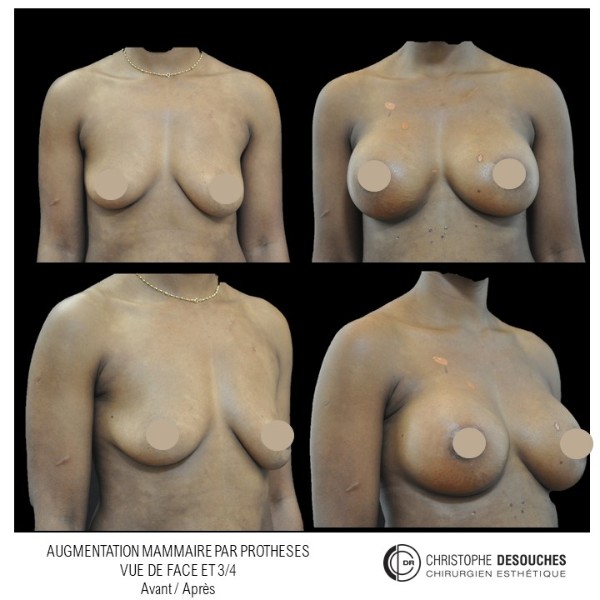
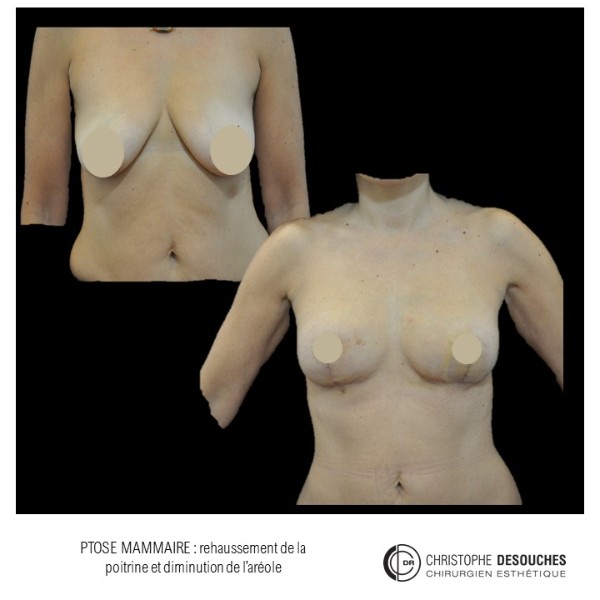
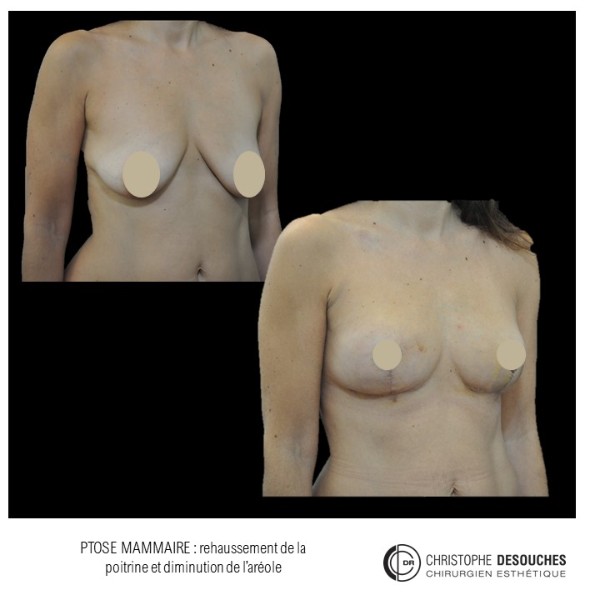
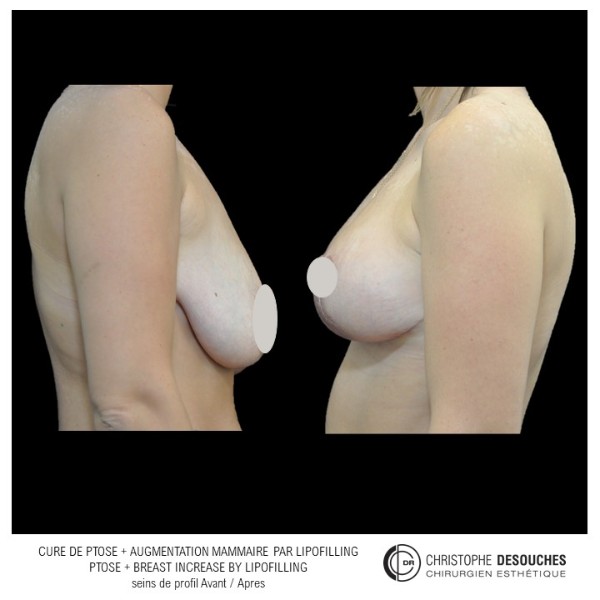
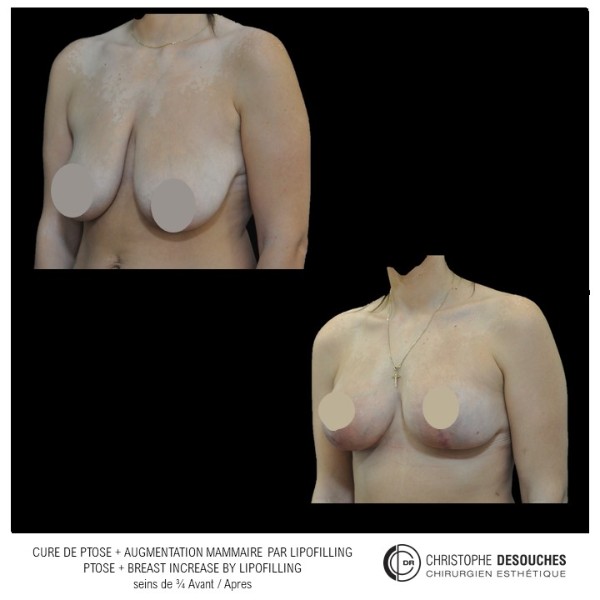
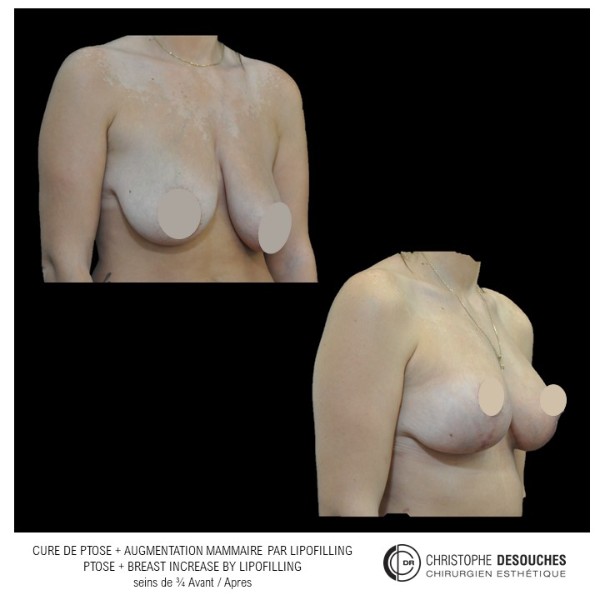
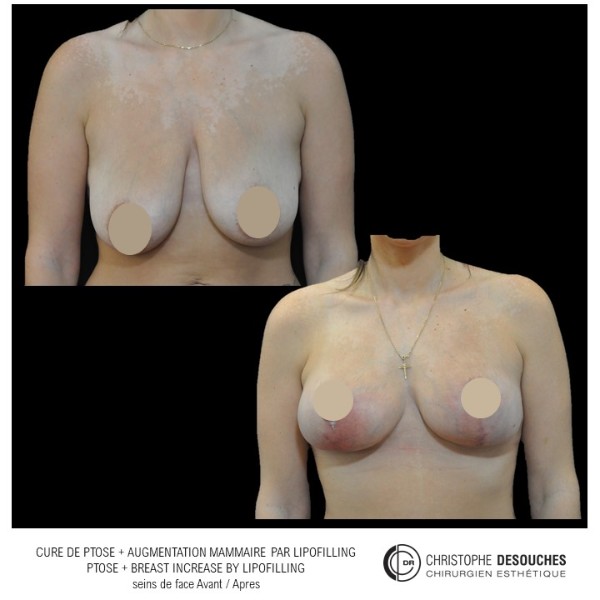
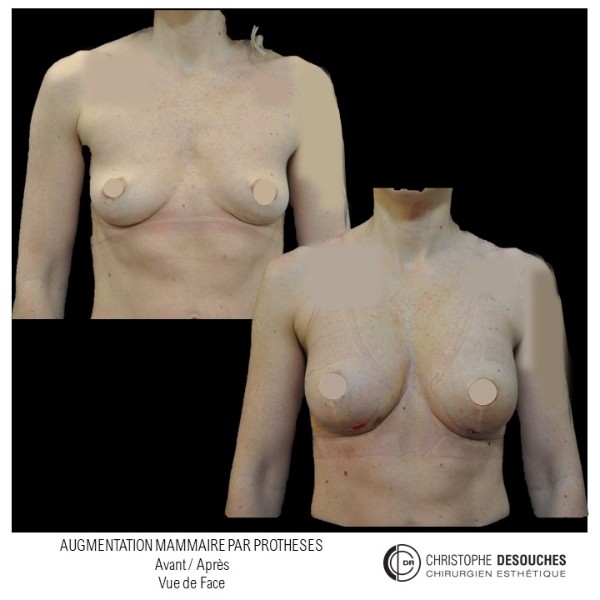
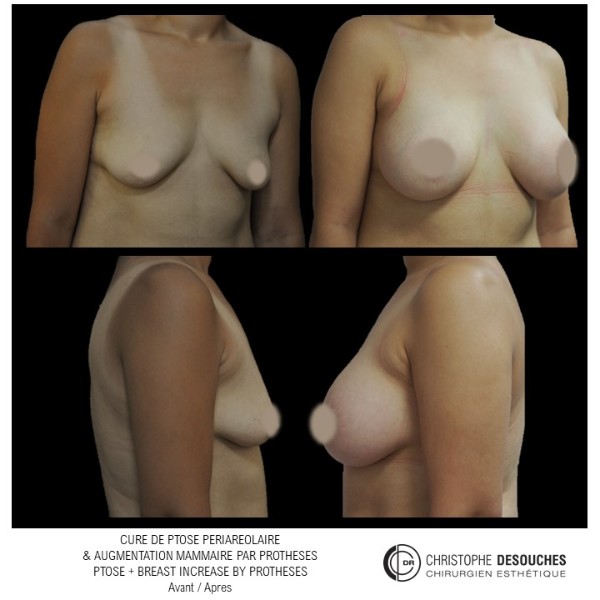
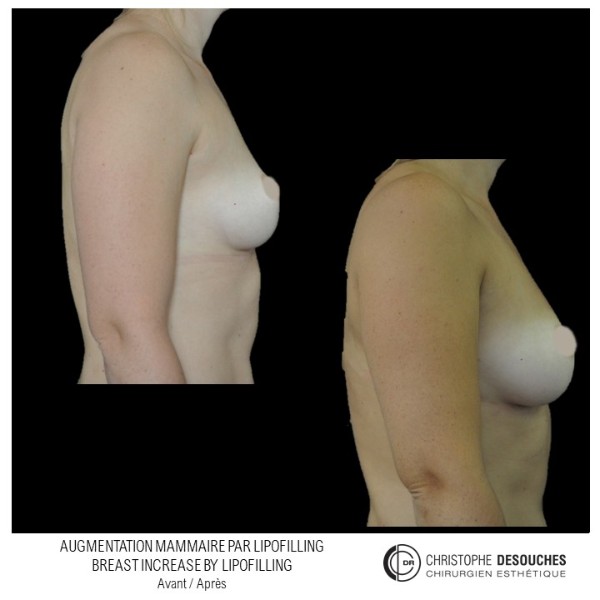
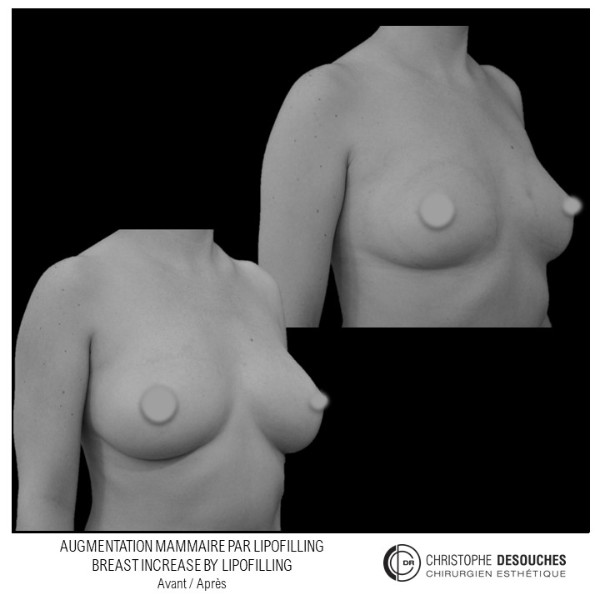
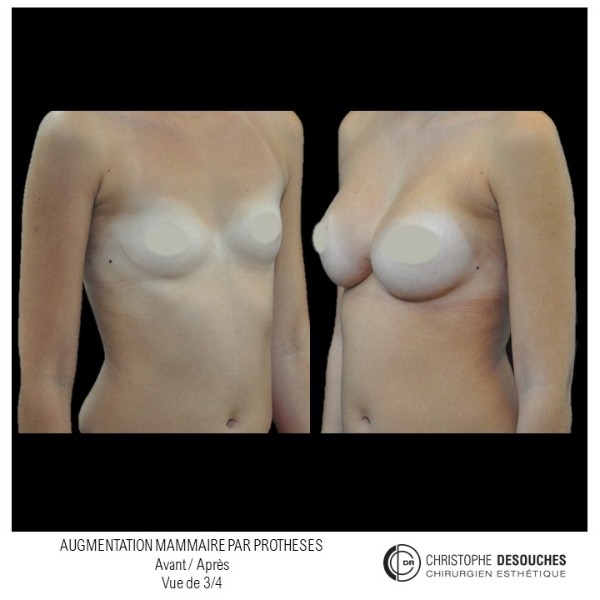
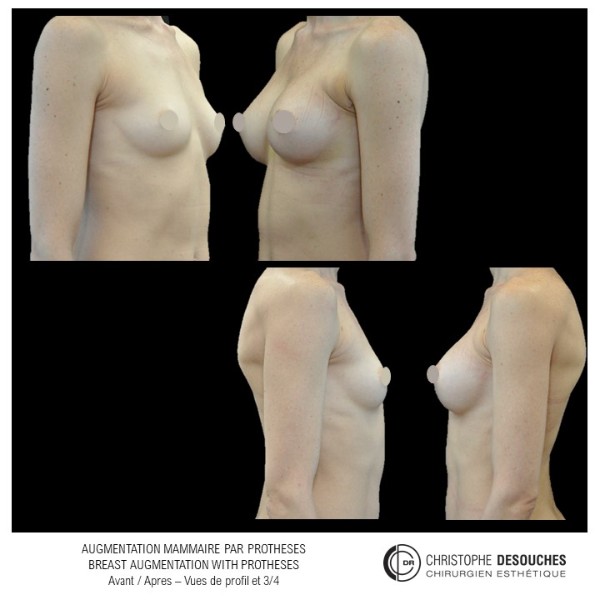
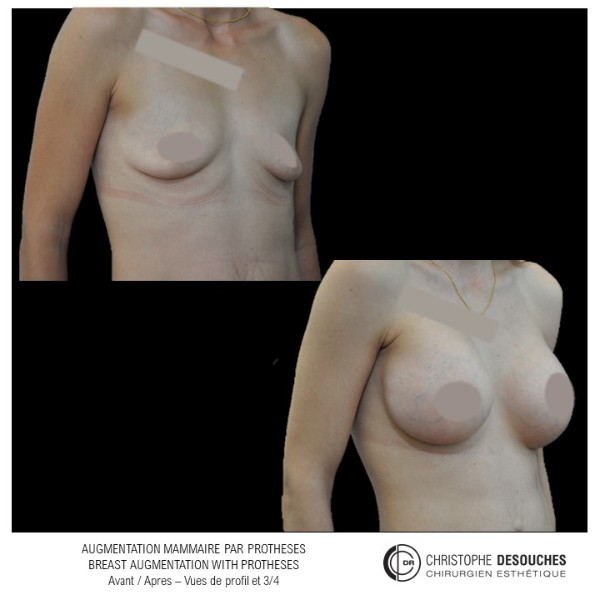
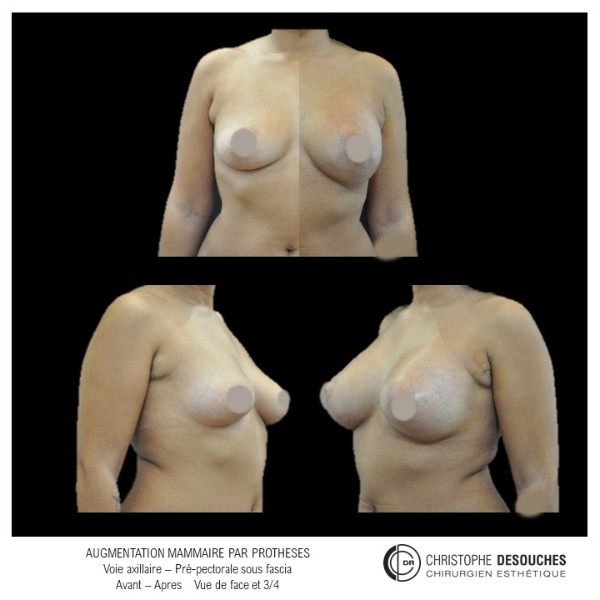
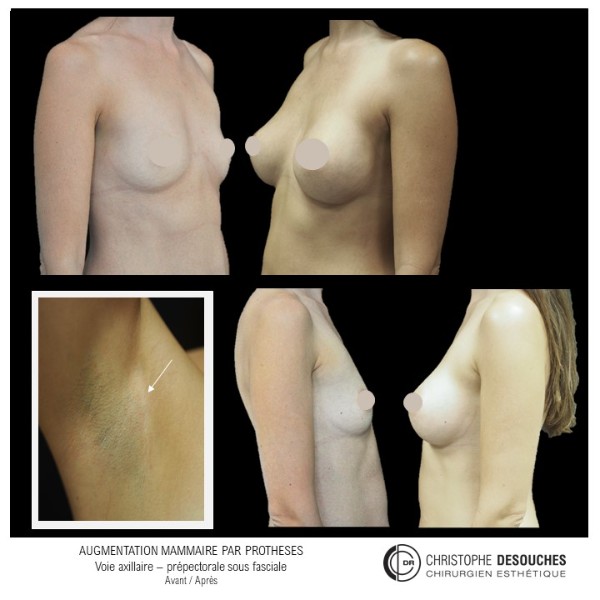
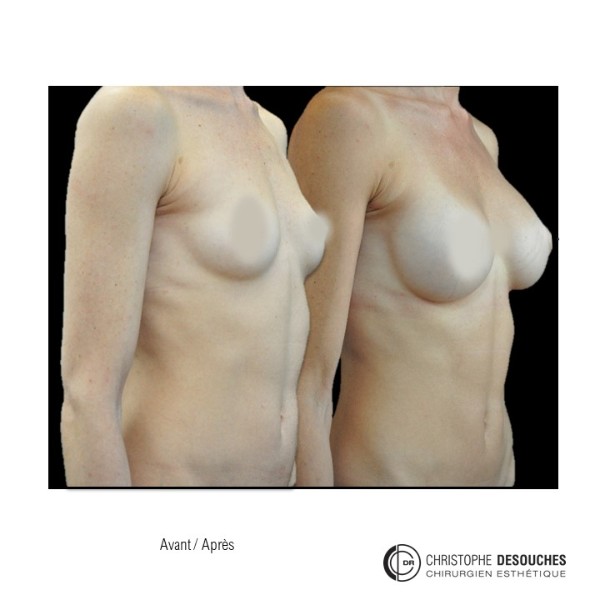
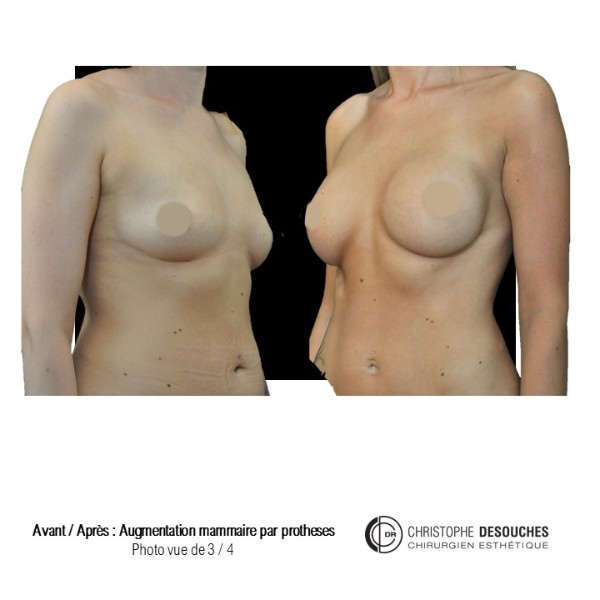
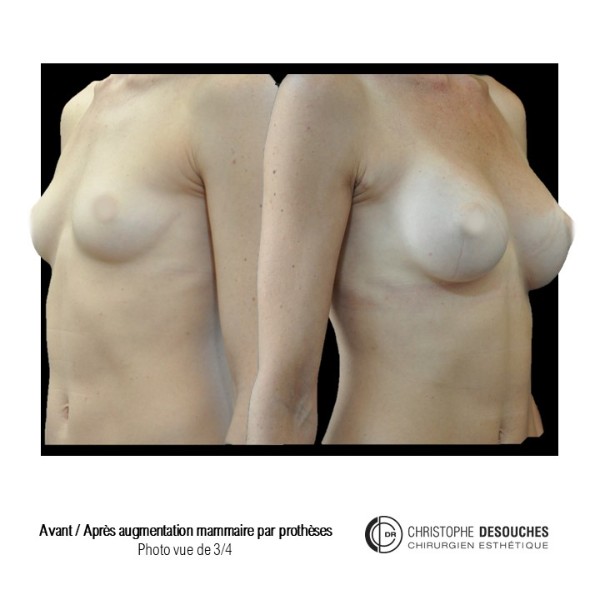
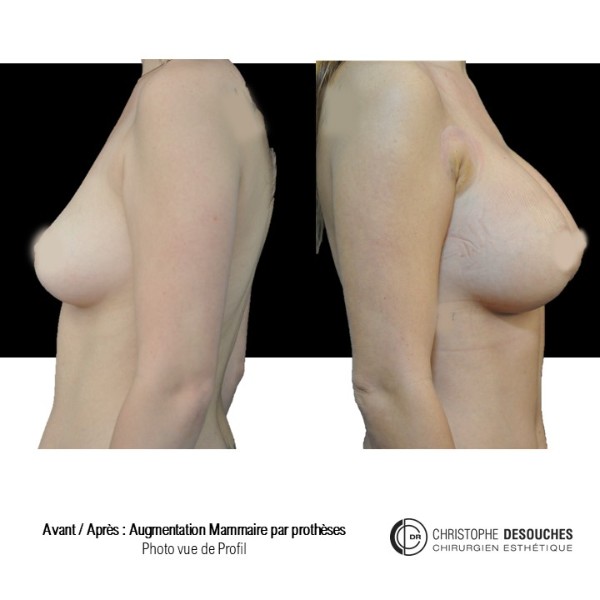
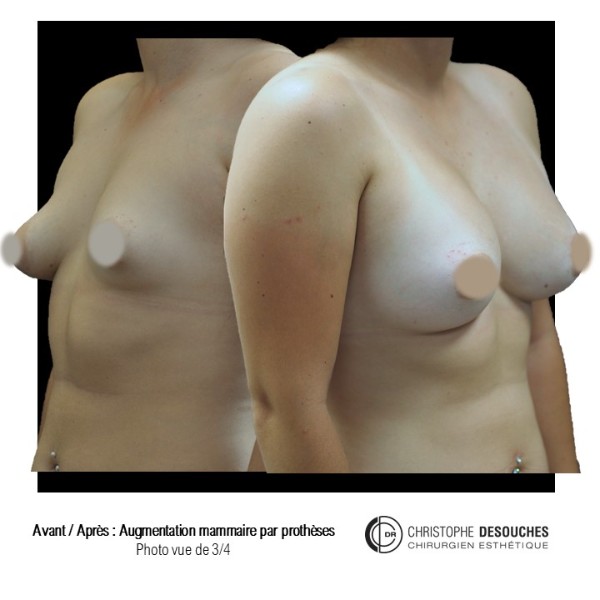
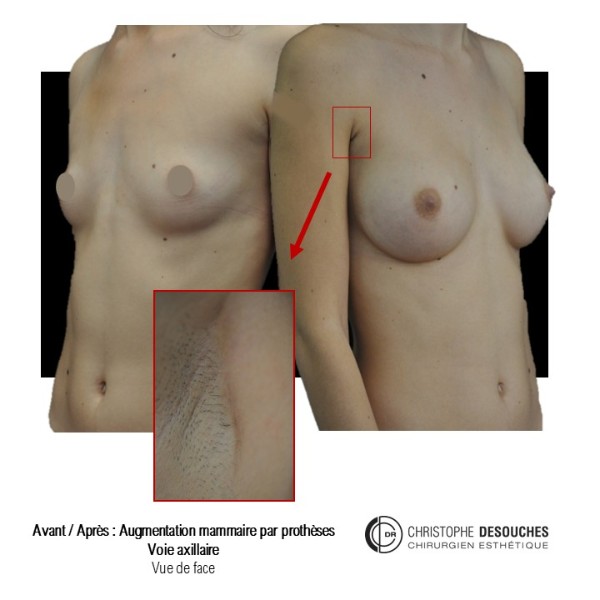
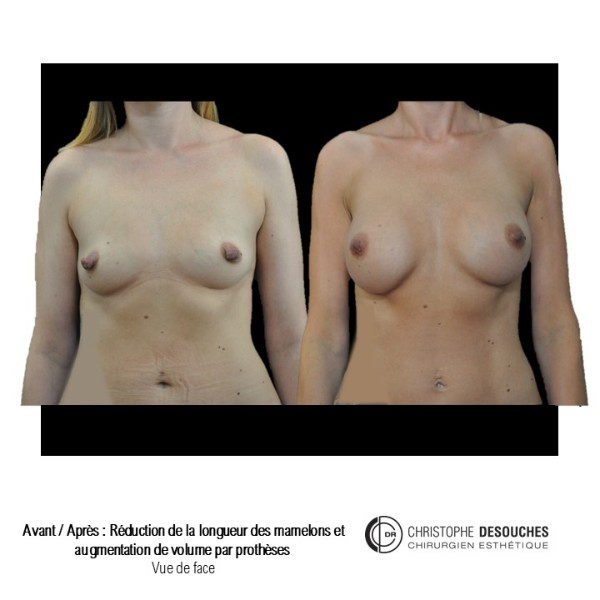
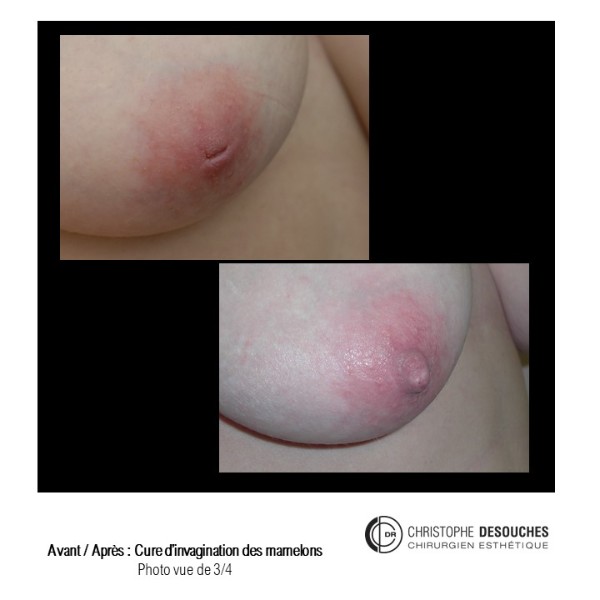
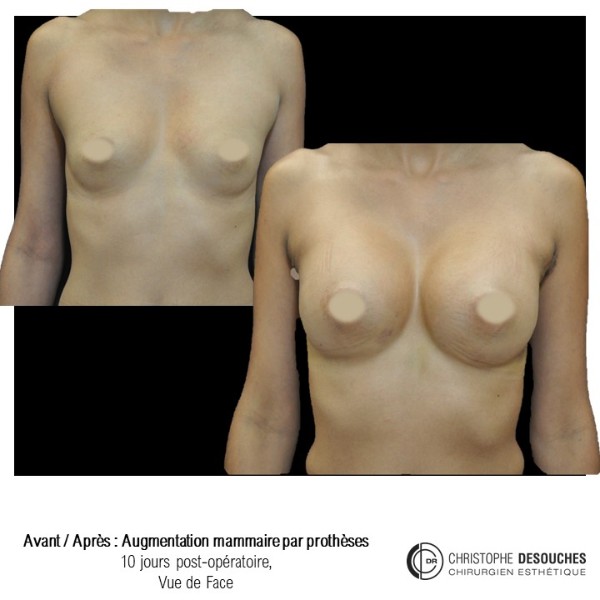
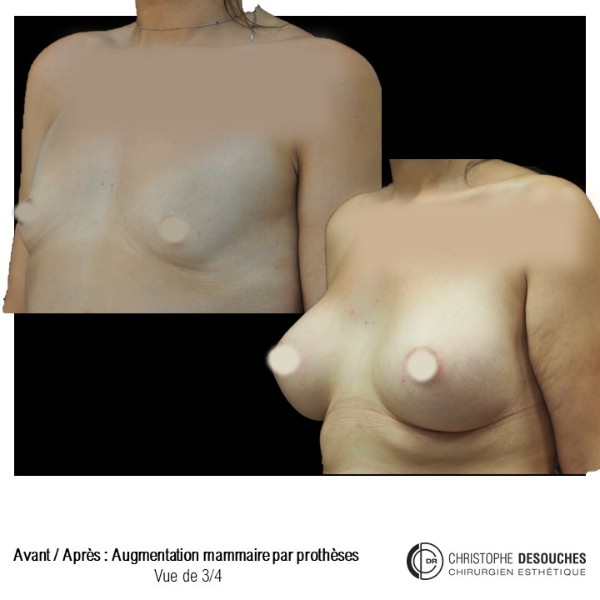
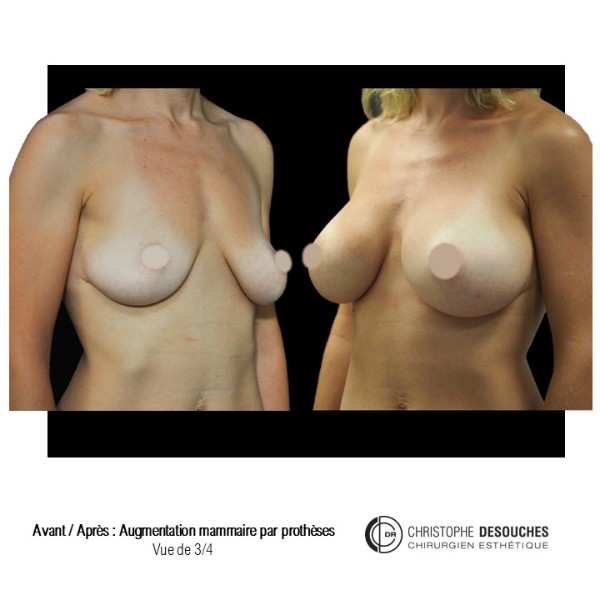
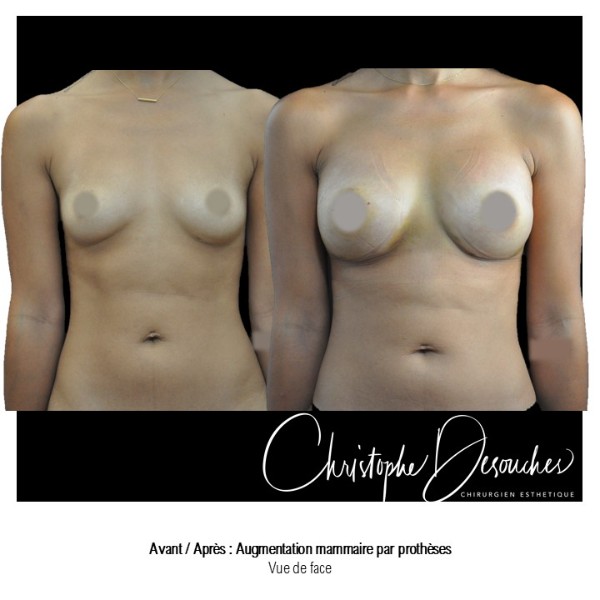
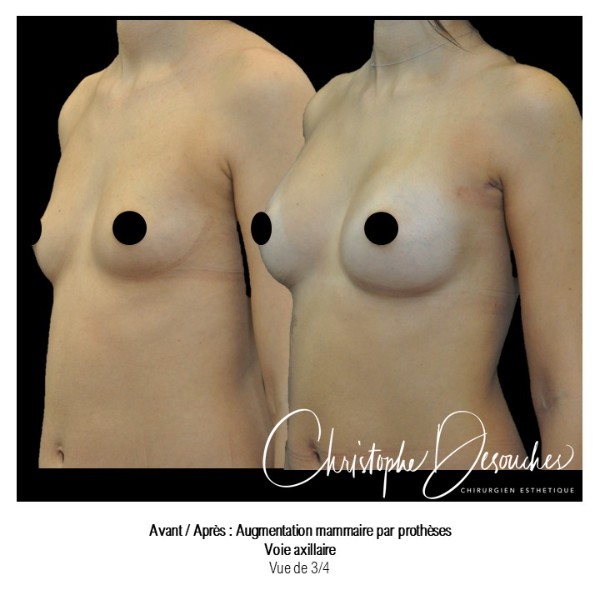
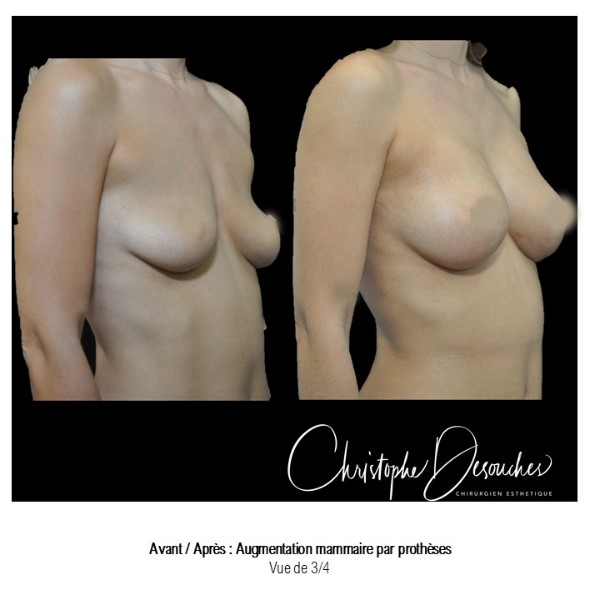
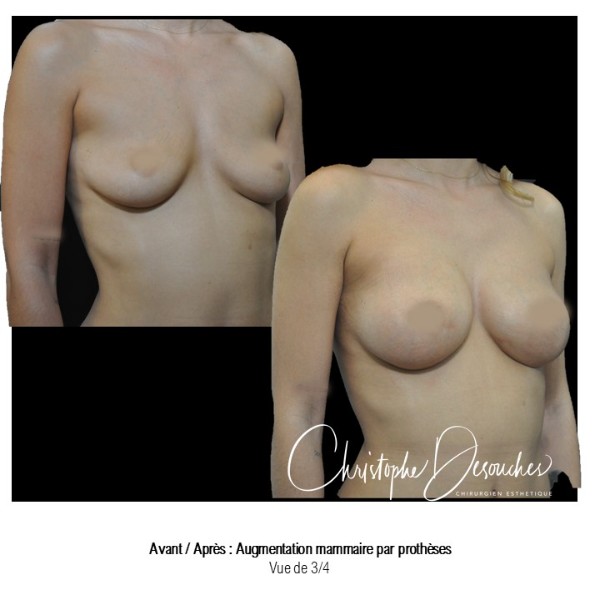
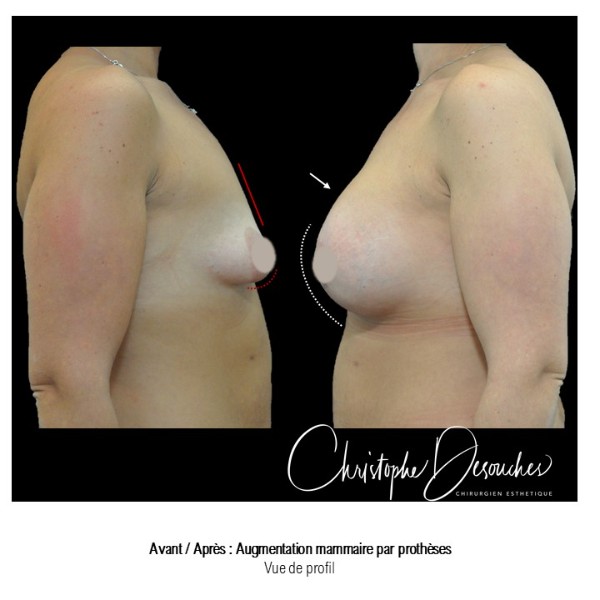
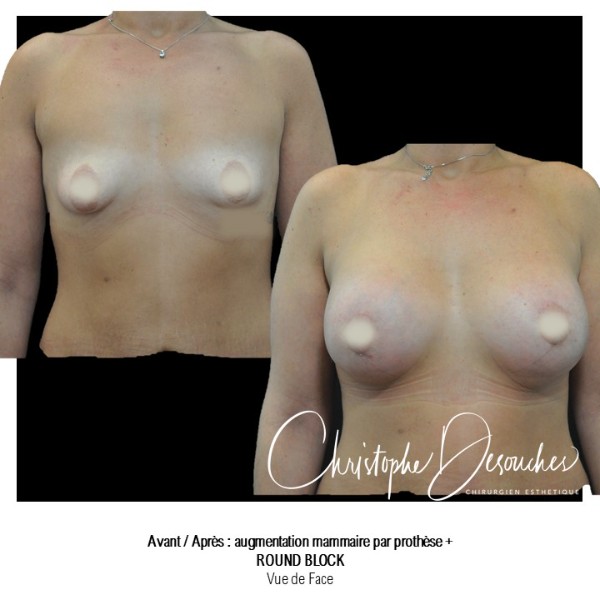
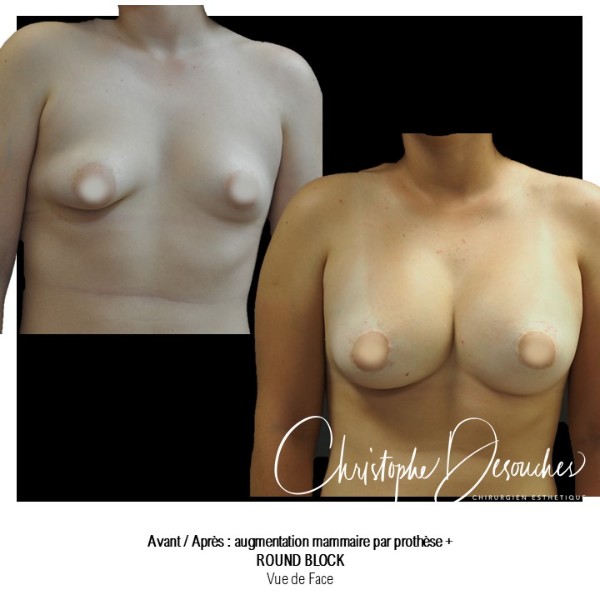
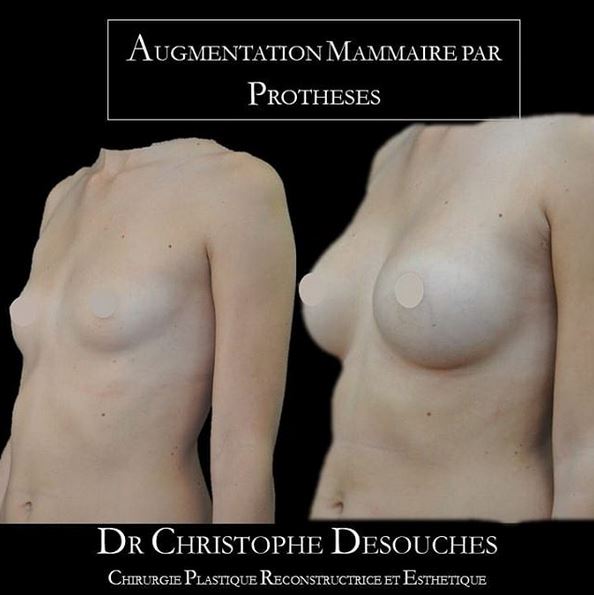
The increase in breast volume by lipofilling consists of injecting one's own adipose tissue into the breast to correct a volume deemed insufficient.
The intervention can be offered when the breasts have not developed sufficiently or when the breast volume has decreased following weight loss or pregnancy.
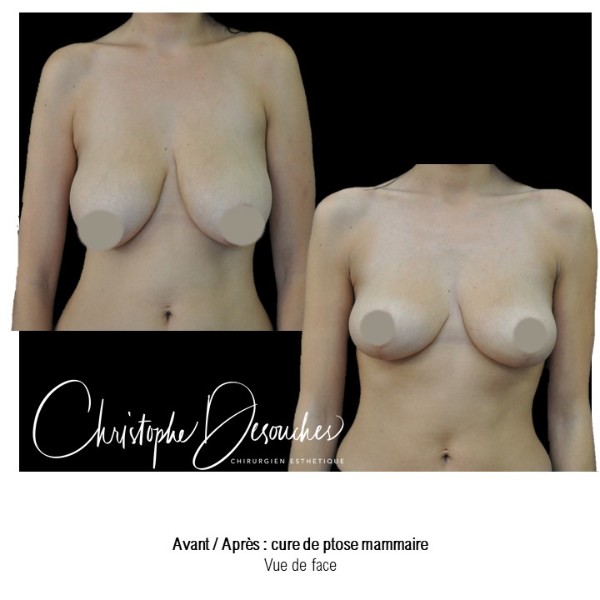
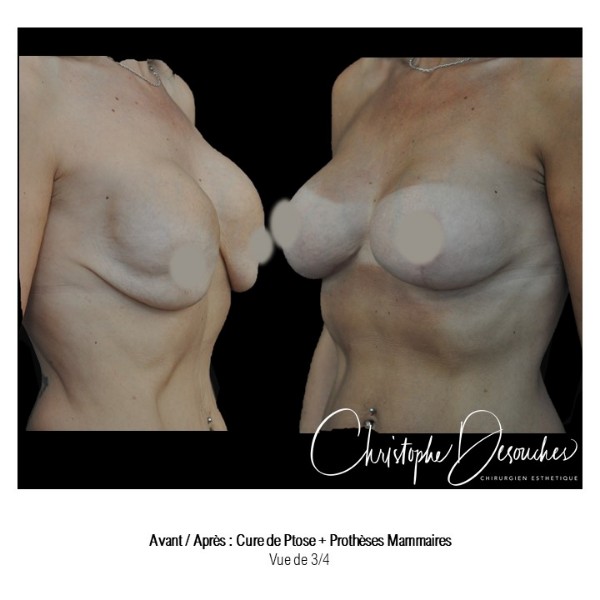
It can also be associated with the correction of breast fall.
However, this surgery cannot be performed in thin, fat-free patients. It is sometimes necessary to perform a second intervention to perfect the result.
Lipofilling: a transfer of fat to the breast
This fat transfer technique is a very well codified intervention used for many years in plastic surgery. Called by different authors lipostructure, liposculpture, lipomodelling or lipofilling of the breast, it consists in removing fat from a donor area (generally the belly, hips or thighs) by liposuction and then reinjecting it with fine cannulas after purification. Spontaneous resorption of approximately 40% of the injected mass occurs explaining the need for over-correction. The result obtained around the 6th month is final.
Currently no scientific argument suggests that the transfer of fat can promote the development of breast cancer. However, it is important not to perform this surgery on a patient with a latent tumor. This is why it is requested to carry out an imaging assessment (mammography and ultrasound) preoperatively and to carry out monitoring at one year and then at two years. During this monitoring, calcifications may be discovered. If in doubt, a biopsy will be performed. It is therefore advisable to reserve this type of surgery for a woman with a minimal risk of familial cancer.
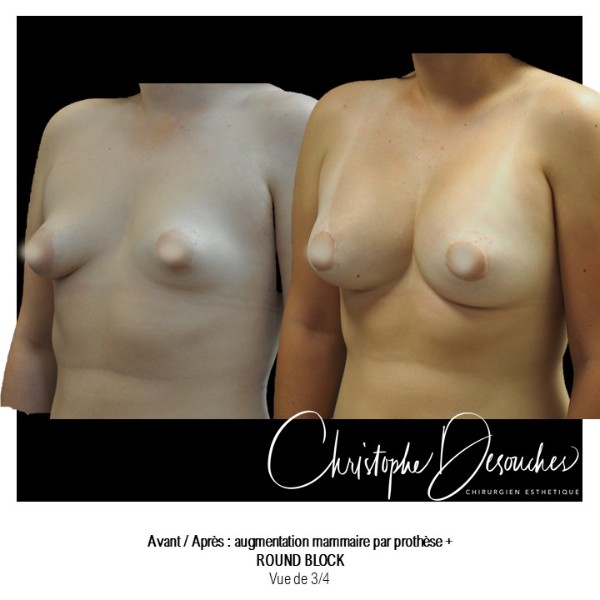
Fat transfer is not indicated for all breast augmentation. It is reserved for women wishing a moderate increase and having sufficient fat capital. This surgery can be performed alone, in addition to a prosthesis augmentation or associated with a ptosis cure (breast lift).
How is breast augmentation performed by lipofilling?
The aim of the procedure is to inject fat into the breast after having taken it from where it is in excess.
The fatty tissue is removed by liposuction in a gentle and atraumatic manner. After purification, the cellular part of the fat removed is reinjected as a coating using small cannulas through puncture-shaped skin incisions.
The procedure is usually performed under general anesthesia. A short hospital stay of one day or one night is sufficient.
How is a lipofilling performed?
The initial consultation
During the initial consultation, you will be offered the various surgical methods that may be suitable for you. A quote will be given to you. This cosmetic surgery cannot be covered by health insurance.
Before the intervention
The anesthetist will be consulted less than a month before the operation.
The radiological assessment (mammography and ultrasound) is performed by a radiologist specializing in breast imaging. If possible, the same radiologist will carry out monitoring examinations after surgery.
No medication containing aspirin should be taken in the 15 days preceding the procedure.
It is imperative to stop smoking at least two months before the surgery, tobacco being a factor in the failure of adipocyte transplant.
It is imperative to remain on an empty stomach (not to eat or drink anything) during the 6 hours preceding the operation.
Before the surgery and the two preceding days, an antiseptic soap will be used for the shower.
After the intervention
The postoperative effects are generally not very painful. Swelling at the donor and recipient sites is often severe and usually takes 15 to 20 days to resolve. Any bruising is visible for one to three weeks. Sun exposure is contraindicated during this period.
After extensive liposuction, a feeling of marked fatigue can be felt over a period of 10 to 15 days. Resumption of professional activity is possible after one week and sporting activity after 4 weeks.
There is a slow absorption of fat which stabilizes around the 6th month. It is on this date that we can assess the final result. A 2nd breast lipofilling session can then be considered in order to optimize the result (in shape or in volume). The costs generated are identical to the first session.
The fatty tissue graft is permanent and the grafted volume follows the volume variations linked to weight changes. In the event of weight loss, the volume of the breasts will decrease and in the event of weight gain, the volume will increase.
The final result of the liposuction is also appreciated from the 6th month.
A follow-up consultation will be necessary at 3 months, 6 months and one year. A radiological assessment identical to the initial assessment will be carried out at 1 year then at 2 years.
What are the risks associated with breast augmentation by lipofilling?
Any surgical procedure, even carried out competently in conditions of maximum safety, carries a risk of complications. There are risks of reaction to the anesthesia. It should be noted that the anesthetic techniques, the products used and the monitoring methods have made immense progress. They offer optimal safety, especially when the intervention is performed outside the emergency room and in a healthy person, but they nevertheless carry the risk of serious complications.
Exceptionally, infection of the injected fat can occur. Antibiotic treatment may be used. In case of collection, a surgical evacuation can be carried out resulting in a scar of one or two centimeters.
Even more exceptionally, pneumothorax can occur, possibly requiring surgical drainage.
Oily cysts may appear in the breast during the procedure. The technical term is cytosteatonecrosis nodule. Completely benign, it can be confirmed by an ultrasound and evacuated by a simple puncture.
Imperfections of results can be observed (asymmetry, irregularities). They can be corrected by another intervention from the 6th month.
When it comes to liposuction, the procedure usually presents very little risk. The risk increases with the volume of fat removed and the number of areas treated during the same operation.
The most important complication is the migration of a clot from a vein in a lower limb (phlebitis) into the bloodstream into the lungs (pulmonary embolism). This complication can, when it is massive, lead to death. Wearing varicose veins, getting up early and possible anticoagulant treatment can prevent this risk. Bruises and infections are rare.
The scars are small in size and usually hidden in the natural folds. The imperfections of results are not absent after liposuction. The result may show asymmetries. Sometimes additional intervention may be necessary.
Breast Augmentation Frequently Asked Questions >